9:48:42 AM | 2/6/2026
The world is moving toward a new multipolar era with opportunities and challenges intertwined. The global economy has again shown resilience beyond expectations despite instability and geopolitical shifts. However, growth and welfare will depend on how each nation manages governance within a new global economic order, facing financial challenges such as tariffs, monetary policy, digital currency, and especially the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). On average, researchers predict that 39% of the existing skills of workers will change or become outdated in the 2025-2030 period.
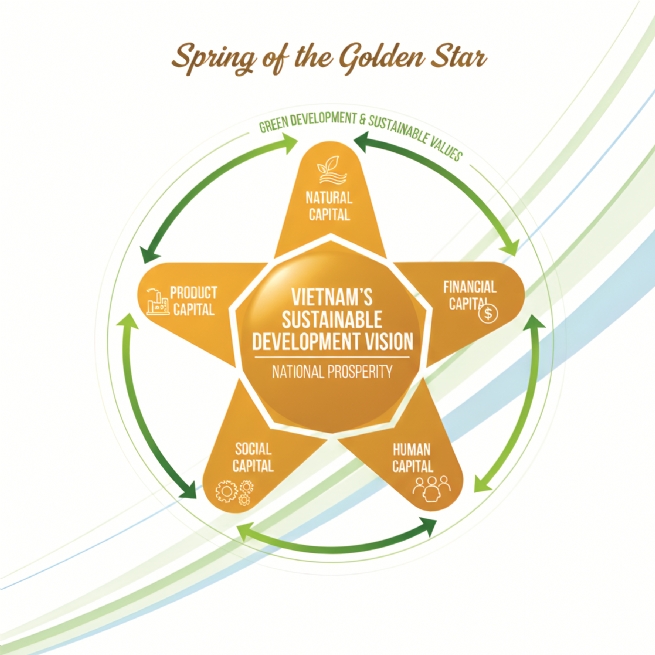
A five-pointed yellow star representing natural, financial, human, social, and product capital for green development and long-term prosperity
Vietnam has entered the New Year on a solid and positive footing. The scale of GDP and export-import turnover has continued to expand. In 2025, GDP exceeded US$510 billion, placing the country 32nd in the world and 4th in ASEAN. Trade turnover ranked 20th globally, while a high trade surplus was maintained. In addition, the 14th Party Congress, guided by the principle of development for stability, stability to promote development, and the ongoing improvement of people’s living standards, together with three strategic breakthroughs, seeks to steer Vietnam toward becoming a developing country with modern industry by 2030.
However, according to development strategists, as a developing country with limited land, a large population, and a long coastline along the East Sea, in order to promote national renewal in the new period, Vietnam should focus on three key areas.
First, planning, vision orientation, and identification of resources: comprehensive socio-economic and environmental planning must be the foundation that links resources, creates fairness and transparency, and serves as the basis to mobilize combined strength. Planning that includes macro indicators and major growth targets will be the guideline for effective resource mobilization, breakthrough creation, innovation promotion, and national development. However, national planning should be built and developed based on a quantitative governance model of five basic resources under the philosophy of the Five Elements, symbolized by a five-pointed yellow star, oriented toward green development and sustainable values through the balance and accumulation of five types of capital: natural, financial, human, social, and product capital, to achieve long-term prosperity.
Second, sustainable governance of resources: good governance will ensure fair access, responsible management, and shared benefits, allowing all forms of capital to grow strongly to create long-term prosperity rather than short-term gains. Important tasks, programs, projects, and works, as well as plans and strategies in national economic development planning, must be integrated with a sustainable governance platform, including management systems and processes to identify, develop, and monitor the five national resources to achieve macro indicators and GDP growth.
Financial resources: in essence, governance of financial capital determines the value of resources and helps analyze the real national capacity to generate cash flow, highly liquid capital, and transparent disbursement to promote economic activities and growth. The State Bank needs appropriate interest rate policies, while state-owned enterprises must maintain a leading role in guiding socio-economic development and take stronger initiative in supporting the private business system to reduce production costs and improve the quality and efficiency of essential products and services, contributing to macroeconomic stability. Moreover, since land belongs to the entire people, a realistic valuation method and suitable tax policy are needed so that citizens can access this resource equally and narrow the wealth gap.
It is necessary to promote the internationalization of the currency through appropriate fiscal and monetary policies, develop international financial centers in Ho Chi Minh City and Da Nang, attract FDI, and shift trade payments to VND, while using free trade agreements to expand the scope of national currency usage, turning the VND into a valuable instrument for storage, exchange, and accounting in the international market.
Natural resources: basic resources such as land, minerals, trees, forests, rivers, lakes, seas, and space, including underground space, must be identified and assessed openly and regularly to ensure fair and reasonable exploitation, accumulation, and prevention of depletion. Vietnam, with 21 of 34 provinces and cities bordering the sea, should strongly develop a strategy toward the East Sea to expand the marine economy and protect national security.
However, complex natural disasters and coastal climate change occurring annually have seriously affected natural resources. Therefore, besides hard products, attention should be paid to soft products in risk management by managing how people and assets interact with disaster-prone areas. Soft products such as documents, planning, strategies, and plans of the Party and Government traditionally contain only two pillars, economy and society, and an additional pillar of environment should be added to ensure that the whole society moves toward the three main pillars of sustainable development.
Human resources: Vietnam, as a populous developing country, should pursue the dual target of GDP growth and employment because high GDP based on capital-intensive sectors will not guarantee jobs, leading to jobless growth and worsening inequality, unemployment, and poverty cycles that cause social instability. Therefore, it is necessary to focus on job-creating growth and ensure good labor conditions, including wages, working environment, housing, transport, health care, and social insurance, combined with comprehensive policies so that economic expansion benefits the large workforce, promotes gender equality, social stability, poverty reduction, and sustainable development, creating a positive cycle of productivity and well-being.
In addition, in the digital era there is a shortage of high-quality human resources. Proactive policies are required to train and develop manpower in digital knowledge and technological skills such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, programming, and cyber security.
Social resources: continuing legal reform, building a law-based state with two-tier local government, and creating frameworks for new areas such as e-government, digital technology, and green energy, remove obstacles and group interests, and ensuring laws have long-term vision, transparency, and fairness for citizens and the economy, turning institutional strength into a core driver and breakthrough for growth.
Completing a transparent market economy with cooperation and fair competition among state, private, and FDI sectors to gradually balance domestic circulation with international trade in the direction of dual circulation. In that process, strengthening domestic economic cycles to improve national competitiveness while using the global market to promote high-value growth.
In the market economy, the factor market provides inputs such as land, labor, capital, and raw materials as the structural backbone for economic development beyond the product market. Therefore, a specialized government agency is needed to research and develop these input markets, especially labor training, recruitment, wages, and land prices in the context of an increasingly internationalized workforce.
For public institutions, it is necessary to gradually streamline and improve the effectiveness of the central and local administrative apparatus, focusing on governance of basic resources, building a leadership team with vision, capacity to mobilize resources, and possessing decisiveness, culture, and ethics.
Product resources: infrastructure is the core of product resources, including man-made assets such as buildings, houses, roads, machinery, and technological systems, which form the essential foundation for economic activities. These inputs, together with financial capital and natural and human resources, are transformed into output products and services, effectively creating added value and supporting the social and organizational functions of social resources.
At the national level, priority should be given to agriculture to ensure food security through investment in smart agriculture infrastructure, applying IoT, AI, and Big Data to manage water resources, operate irrigation efficiently, conserve resources, and raise productivity. Green and sustainable agriculture should be developed with a focus on organic production, ecological balance, and environmental protection, along with digital transformation through remote management and traceability. Moreover, besides traditional energy, it is necessary to promote green energy transition and emission reduction, including renewable and nuclear energy. Attention must be paid to developing transport and logistics systems of railways, expressways, waterways, and aviation, connecting localities and international routes.
Leading economic centers such as Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City need to strongly develop public transport infrastructure, reduce congestion, and improve water supply, drainage, and environmental treatment systems to raise urban living quality.
Especially, important national industries must be modernized, building infrastructure for the digital industry such as high-speed internet, strong IoT networks, cloud and data platforms, AI, and cyber security.
However, in the process of infrastructure development for key industries, attention should be paid to a dual-use industrial strategy to ensure national defense and security.

Leading economic centers such as Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City need to upgrade public transport, ease congestion, and strengthen water and environmental infrastructure to improve urban living quality
Third, international cooperation strategy: in the context of deep integration, leadership qualities related to diplomacy and international relations have become more important. Leaders must engage in effective diplomacy because both partners and competitors play significant roles. Competitors promote innovation, efficiency, and self-improvement through pressure and the standards of developed markets, while partners provide shared resources, wider market access, cost savings, and supply chain cooperation to address major challenges, expand markets, and create new opportunities that no side can achieve alone, thereby fostering growth. In that process, it is necessary to build strong relations with other countries, especially ASEAN neighbors, Northeast Asian nations, and comprehensive strategic partners, while actively participating in international organizations to protect economic interests and national security. These activities include attracting foreign investment, accessing advanced technology, promoting trade, and international cooperation for sustainable development. Negotiation skills must also be improved in the context of reciprocal tariff policies disrupting multilateral trade institutions and affecting global production and supply chains.
The synchronized and effective implementation of the three key areas at the beginning of the Lunar Year 2026, with its symbol of agility and energy, will certainly be a sign of a successful year. This will open a new era, generate strong momentum, contribute to the successful realization of the 2026-2030 plan and the national vision to 2050, bring sustainable development, and gradually improve the living standards of the people.
Dr. Doan Duy Khuong
Source: Vietnam Business Forum